|
0 Comments
The GLP-1 receptor agonist market, a critical segment of the pharmaceutical industry, is poised for significant transformations as it continues to address the needs of patients with type 2 diabetes. This dynamic market has seen impressive growth and innovation, but it also faces unique challenges that warrant attention and proactive strategies. Combination Therapies: Combination therapies, involving the use of GLP-1 receptor agonists in conjunction with other diabetes medications, are becoming more common. This approach can provide synergistic effects and better blood sugar control, offering patients comprehensive treatment strategies.
Personalized Treatment: The concept of personalized medicine is gaining traction in the GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Market. Advances in genetics and molecular biology are enabling healthcare providers to tailor treatment plans to individual patients' needs, maximizing the effectiveness of these medications. Digital Health Solutions: The integration of digital health solutions, such as mobile apps and wearable devices, is transforming how patients and healthcare professionals manage diabetes. These technologies can assist with medication adherence, track blood sugar levels, and provide real-time insights into patients' health status. Affordability and Access: Despite the market's growth, affordability and access to GLP-1 receptor agonists remain challenges for many patients. Developing cost-effective options and collaborating with healthcare systems to improve access will be crucial to ensuring equitable treatment for all. Long-term Safety and Efficacy: While the cardiovascular benefits of GLP-1 receptor agonists are well-established, the long-term safety and efficacy of these medications require continuous monitoring. Post-market surveillance and research are essential to identify any potential adverse effects over extended periods. Patient Education: Educating patients about the benefits, proper usage, and potential side effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists is vital. Empowering patients to make informed decisions about their treatment can improve adherence and overall treatment outcomes. As the GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Market navigates the future, collaboration among pharmaceutical companies, healthcare providers, regulators, and patient advocacy groups will be instrumental. By working together, these stakeholders can overcome challenges and capitalize on emerging trends to improve the lives of individuals with type 2 diabetes. In conclusion, the GLP-1 receptor agonist market's journey is one of growth, innovation, and adaptation. While trends like personalized treatment and digital health solutions hold promise, addressing challenges related to affordability, safety, and patient education remains crucial. Through sustained efforts and a patient-centered approach, the market can continue to evolve and positively impact the lives of millions affected by type 2 diabetes. In recent years, bath bombs have become a beloved sensation, transforming ordinary baths into a luxurious and therapeutic experience. These colorful spheres of relaxation bring a touch of magic and a burst of delightful aromas to our daily routines. Bath bombs are not just fizzy fun, but they also offer numerous benefits for our physical and mental well-being. In this article, we will dive into the captivating world of bath bombs, exploring their history, ingredients, creation process, benefits, and the eco-friendly movement surrounding them.
Bath Bombs may seem like a contemporary invention, but their origins can be traced back to the ancient world. The concept of using natural salts, oils, and aromatic herbs for bathing has existed for centuries in various cultures, including the Egyptians, Greeks, and Romans. These early civilizations recognized the therapeutic properties of such ingredients in rejuvenating the body and mind. The modern bath bomb, as we know it today, was invented in the late 1980s by Lush Cosmetics co-founder Mo Constantine. Combining her passion for art and chemistry, she created the first colorful and effervescent bath bomb, revolutionizing the bathing experience for millions around the world. The allure of Bath Bombs lies in their enchanting transformation as they dissolve in water, releasing vibrant colors, delightful scents, and nourishing ingredients. Crafting bath bombs is both an art and a science. The primary ingredients of bath bombs include baking soda (sodium bicarbonate) and citric acid, which react when combined with water to create the fizzing effect. Additionally, essential oils, natural colorants, Epsom salts, and various other nourishing elements are added to create unique blends. The process of making bath bombs requires precise measurements and careful mixing to achieve the perfect balance of fizz, color, and scent. Artisans often handcraft these creations, pouring their creativity and passion into each one. Aromatherapy: Essential oils infused in bath bombs can have calming, invigorating, or uplifting effects on the mind, depending on the chosen scent. Muscle and Joint Relief: Bath bombs with Epsom salts can aid in reducing inflammation and soothing sore muscles and joints. As the world becomes more environmentally conscious, the bath bomb industry has also embraced sustainability. Traditional Bath Bombs often contain synthetic dyes, preservatives, and artificial fragrances, which can be harmful to both the environment and our bodies. To address these concerns, many manufacturers are transitioning towards eco-friendly bath bombs made with natural and organic ingredients. These eco-conscious bath bombs utilize biodegradable glitter, plant-based colorants, and responsibly sourced essential oils, reducing their ecological footprint while still providing a luxurious bathing experience. Bath Bombs have captured the hearts of people worldwide, turning bath time into a delightful and rejuvenating ritual. From their ancient roots to modern-day creations, bath bombs have come a long way, captivating us with their enchanting fizz and intoxicating scents. Beyond their alluring appearance, bath bombs offer therapeutic benefits that can enhance our well-being in numerous ways. As the bath bomb industry evolves, embracing sustainability becomes paramount, allowing us to indulge in these colorful spheres of magic with a clear conscience. In mission-critical operations, such as military missions, disaster response, or exploration in harsh terrains, rugged displays play a pivotal role in delivering real-time data and maintaining situational awareness. Let's explore how rugged displays enhance these operations: Military Applications: Military personnel rely on rugged displays for tactical communication, intelligence gathering, and navigation in challenging environments.These displays can withstand the constant vibrations and temperature variations experienced during transportation.
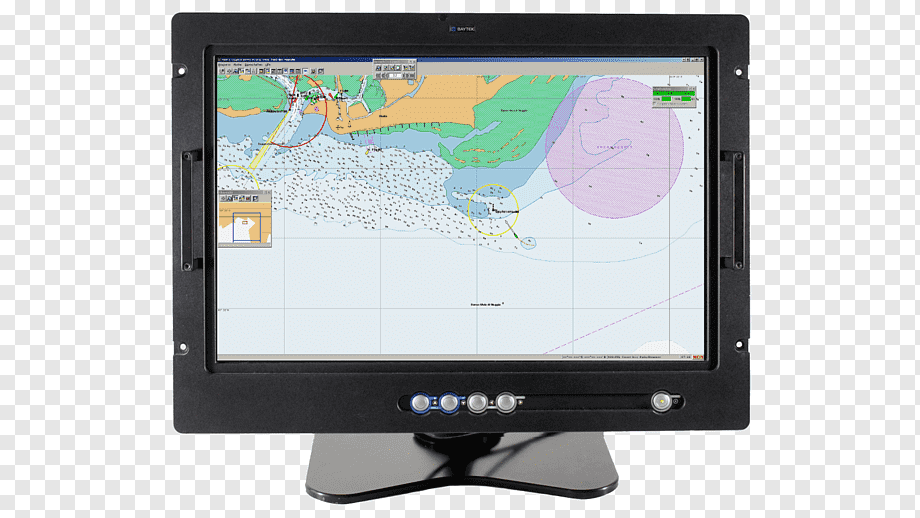
Industrial Applications: Industries like construction and mining often require displays that can withstand rugged conditions on job sites. Rugged Display mounted on heavy machinery help operators monitor equipment performance and enhance overall safety. Outdoor Recreation: Rugged displays have found their way into the outdoor adventure market, catering to hikers, campers, and extreme sports enthusiasts. These displays provide GPS navigation, weather updates, and other outdoor-specific features. Rugged displays ensure continuous functionality, minimize downtime, and contribute to the success of critical operations in various industries. Their ability to withstand the harshest conditions ensures that vital information is always accessible when it matters most. Sunlight Readability: Many Rugged Display boast exceptional sunlight readability, employing innovative technologies like transflective and optically bonded displays. These technologies minimize glare and reflections, ensuring clear visibility even in bright outdoor settings. Military and Defense: Rugged displays play a crucial role in military operations, where reliability and readability are essential in challenging terrains and extreme climates. They are used in military vehicles, aircraft, and portable devices used by soldiers in the field. Industrial Automation: Rugged Display find extensive use in industrial automation and manufacturing processes, where they can withstand harsh conditions such as temperature variations, vibrations, and exposure to dust and chemicals. Transportation: In transportation sectors like aviation, maritime, and railway, rugged displays are employed in control panels, cockpit instrumentation, and on-board information systems, where durability and reliability are paramount. Outdoor Adventure and Sports: Rugged Display have also become popular among outdoor enthusiasts and athletes, as they can withstand the rigors of outdoor adventures, extreme sports, and marine activities. Medical and Healthcare: In medical environments, where hygiene and sterility are vital, rugged displays with high IP ratings are used in operating rooms, emergency response vehicles, and medical equipment exposed to various environmental factors. Public Safety and First Responders: Rugged displays are employed in police cars, fire trucks, and other emergency response vehicles, enabling real-time communication and data access in critical situations. Rugged Display have undoubtedly ushered in a new era of resilience in the tech world. Their unmatched durability, reliability, and adaptability have made them indispensable across various industries, transforming the way we interact with technology in harsh and demanding environments. As technology continues to advance, we can expect further innovations in rugged displays, making them an even more integral part of our modern lives. Whether it's military missions, industrial automation, or outdoor adventures, rugged displays are the steadfast companions that enable us to push boundaries and achieve greater heights. Weather Radar Is Used In Meteorology for Understanding Present and Future Weather Conditions7/25/2023 Weather Radar is a remarkable technology that has revolutionized our understanding of atmospheric phenomena. It plays a pivotal role in meteorology, aiding in weather forecasting, severe weather detection, and aviation safety. By emitting radio waves into the atmosphere and analyzing their echoes, weather radar provides valuable insights into precipitation patterns, storm systems, and other weather events.
Weather Radar operates on the principle of radio wave reflection and transmission. It sends out pulses of radio waves into the atmosphere, and when these waves encounter objects like raindrops, snowflakes, or hailstones, they scatter in various directions. A part of these scattered waves returns to the radar as echoes. The radar system processes these echoes to determine the location, intensity, and movement of precipitation. The data collected from different radar sites are then combined to create a comprehensive image of weather patterns across a wide area. One significant advancement in Weather Radar technology is the integration of the Doppler Effect. The Doppler Effect allows the radar to measure the velocity of precipitation particles, helping meteorologists understand the motion of weather systems. By analyzing the frequency shift in the radar waves caused by moving precipitation, Doppler weather radar can identify wind patterns and differentiate between rain, snow, and hail. This capability is crucial for detecting severe weather phenomena, such as tornadoes and thunderstorms. There are primarily two types of weather radar: the pulse radar and the Doppler radar. Pulse radars emit short bursts of energy and measure the time it takes for the echoes to return, providing information about the distance of the precipitation. On the other hand, Doppler radars use continuous waves and analyze the frequency shifts to determine the velocity of the precipitation particles. Combining these two types of radar provides a more comprehensive understanding of weather conditions. Weather Radar plays a central role in modern weather forecasting. By tracking the movement of weather systems, meteorologists can predict the arrival and intensity of precipitation, identify potential storm formations, and issue timely warnings to the public. Doppler radar's ability to detect wind patterns and analyze storm movements aids in the identification of severe weather events like tornadoes, hurricanes, and thunderstorms. This helps in issuing severe weather warnings to keep communities safe. A Weather Radar is vital for aviation safety, allowing pilots to navigate around areas of turbulence or severe weather. It also helps air traffic controllers manage flights efficiently and avoid hazardous weather conditions. Weather radar assists in monitoring river and stream levels, particularly during heavy rainfall and flooding events. This information aids in flood forecasting and management. Farmers rely on weather radar data to make informed decisions about irrigation, planting, and harvesting. Radar information helps them anticipate rain patterns and prepare for adverse weather conditions. Weather radar data is valuable for climate researchers studying long-term weather patterns and trends. It helps in understanding climate change and its potential impacts on different regions. While Weather Radar is a powerful tool, it does have limitations and faces certain challenges. One significant limitation is its inability to directly measure certain weather parameters, such as temperature, humidity, and atmospheric pressure. Additionally, radar beams can be attenuated or weakened as they pass through intense precipitation, leading to data gaps in areas of heavy rainfall. The accuracy of weather radar is also influenced by factors like the radar's location, beam height, and calibration. Interference from ground clutter and non-meteorological objects can further impact radar readings, requiring skilled interpretation by meteorologists. Performance excellence is a critical requirement for technical textiles, as they are often employed in demanding applications. Textile Chemicals for Technical Textiles offer a range of solutions to enhance the performance characteristics of these specialized fabrics. One essential class of chemicals used for performance enhancement is moisture management agents. These chemicals help in wicking away moisture from the fabric's surface, keeping the wearer dry and comfortable. They are especially valuable in sportswear and outdoor clothing, where moisture control is crucial. Additionally, textile chemicals can provide thermal insulation properties to technical textiles.
Textile Chemicals for Technical Textiles also aid in the dyeing and printing processes of technical textiles. They ensure vibrant colors, colorfastness, and excellent print quality. Additionally, chemicals like sizing agents and lubricants are used to improve the weaving and processing of these fabrics. Furthermore, textile chemicals contribute to the antimicrobial and antistatic properties of technical textiles, making them suitable for medical and electronic applications. These chemicals inhibit the growth of bacteria and reduce static charges. textile chemicals are vital for the production of technical textiles, providing them with enhanced properties and functionalities necessary for diverse industrial applications. In healthcare and medical applications, technical textiles with anti-bacterial and anti-microbial properties play a crucial role in preventing the spread of infections. Textile chemicals are designed to inhibit the growth of bacteria and microorganisms on the fabric surface, ensuring hygiene and reducing the risk of contamination. Such treated textiles find applications in hospital linens, surgical gowns, wound dressings, and other medical devices. Textile Chemicals for Technical Textiles can also provide technical textiles with effective UV protection, safeguarding individuals from harmful sun rays. These chemicals either absorb or reflect UV radiation, reducing its penetration through the fabric. Technical textiles treated with UV protection chemicals are commonly used in outdoor apparel, awnings, and sunshades, where prolonged exposure to sunlight is expected. To enhance the durability and lifespan of technical textiles, manufacturers rely on textile chemicals that improve abrasion resistance. These chemicals create a protective layer on the fabric surface, reducing wear and tear caused by friction, thereby extending the product's lifespan. This property is particularly valuable in industrial textiles, geotextiles, and automotive applications, where textiles are subjected to harsh conditions. Textile Chemicals for Technical Textiles can be utilized to confer conductive and electrostatic properties to technical textiles. These properties are essential in various sectors, including electronics, aerospace, and automotive, where textiles are integrated into advanced systems. By incorporating conductive chemicals, technical textiles can be used in applications such as electromagnetic shielding, sensors, and wearable electronics. Textile Chemicals for Technical Textiles not only enhance the performance of technical textiles but also improve their aesthetic appeal. Chemicals used in dyeing and printing processes ensure color fastness, vibrant prints, and improved ink penetration. These enhancements allow technical textiles to meet the visual and design requirements of industries such as fashion, home furnishings, and interior design. Textile Chemicals for Technical Textiles have revolutionized the capabilities and applications of modern textiles. With their ability to provide waterproofing, flame retardancy, anti-bacterial properties, UV protection, abrasion resistance, conductivity, and improved dyeing and printing, these chemicals enable technical textiles to excel in diverse industries. By continuously pushing the boundaries of innovation, textile chemical manufacturers and researchers play a vital role in advancing the performance, functionality, and sustainability of technical textiles. Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) coatings have proven to be a game-changer in the field of optics, revolutionizing the performance of various optical components. Whether it's lenses, mirrors, or filters, PVD coatings offer significant advantages in terms of optical properties and durability. One of the key benefits of Physical Vapor Deposition coatings in optics is the ability to control the refractive index. By carefully selecting the deposition parameters, engineers can tailor the refractive index to achieve desired optical characteristics, such as anti-reflective coatings that minimize light reflection and increase transmission.
The versatility of PVD enables the deposition of coatings with specific properties tailored to the application. For example, engineers can create lubricious coatings that reduce friction and enhance sliding behavior or coatings with high hardness for resistance against abrasive wear. Physical Vapour Deposition coatings also offer excellent corrosion resistance, making them ideal for components exposed to harsh environments. These coatings can protect against oxidation, chemical reactions, and moisture, ensuring the integrity of critical parts. Physical Vapor Deposition coatings have revolutionized the field of wear-resistant coatings, providing exceptional hardness, adhesion, and corrosion resistance. The versatility of PVD enables tailor-made coatings for specific applications, ensuring enhanced performance and extended lifespan of components in diverse industries. Ion plating combines the principles of evaporation and sputtering. The process involves the vaporization of a solid material through electron beam bombardment, followed by the ionization of the vaporized atoms. The ions are then accelerated towards the substrate, resulting in a denser and more adherent film. Physical Vapor Deposition finds applications in various industries due to its ability to enhance surface properties. Some of the most common applications include: Optical Coatings: PVD is widely used in the production of optical coatings, such as anti-reflective coatings for lenses, mirrors, and displays. These coatings reduce unwanted reflections and improve light transmission, enhancing the overall performance of optical systems. Decorative Coatings: Physical Vapour Deposition is utilized to create decorative coatings on a wide range of products, including jewelry, watches, and consumer electronics. The process allows for the deposition of thin films of metals such as gold, silver, and titanium, resulting in attractive and durable finishes. Wear and Corrosion Protection: PVD coatings are known for their excellent wear and corrosion resistance properties. They are commonly applied to cutting tools, machine components, and automotive parts to improve their lifespan and performance. Semiconductor Industry: PVD plays a crucial role in the manufacturing of semiconductors and integrated circuits. It is used for metal deposition during the fabrication of interconnects, contacts, and barrier layers. As technology advances, so does the potential for further innovation in PVD. Here are some exciting trends and advancements that may shape the future of Physical Vapor Deposition: Nanostructured Coatings: Researchers are exploring the development of nanostructured PVD coatings, where thin films are engineered at the nanoscale. These coatings exhibit unique properties, such as enhanced hardness, improved adhesion, and increased resistance to fatigue. Physical Vapor Deposition has revolutionized the field of thin film coatings, offering a wide range of applications and opportunities for innovation. Its ability to deposit high-quality thin films with improved properties has made it a preferred choice in industries such as optics, electronics, and automotive. As we look towards the future, the ongoing research and development in PVD techniques promise exciting advancements that will unlock new possibilities and propel the industry forward. The constant pursuit of efficiency and profitability in the oil refining industry has led to significant advancements in refinery catalysts. Refinery Catalyst are designed to maximize conversion rates, yield high-quality products, and minimize operating costs. In recent years, novel catalyst formulations and manufacturing techniques have emerged, leading to improved catalyst performance. Advanced catalysts exhibit higher activity, selectivity, and stability, enabling enhanced conversion of crude oil into valuable products. They offer superior resistance to deactivation and fouling, prolonging catalyst lifespan and reducing downtime for maintenance.
Another challenge is catalyst selection and optimization. Refineries must choose catalysts that are tailored to their specific processes, operating conditions, and feedstock characteristics. Extensive research, pilot testing, and collaboration with Refinery Catalyst suppliers are essential to ensure the best catalyst choice. To tackle these challenges, refineries are investing in advanced catalyst monitoring systems. These systems provide real-time data on catalyst performance, allowing for proactive maintenance and optimization. The primary function of a Refinery Catalyst is to enhance the selectivity, efficiency, and speed of chemical reactions that occur during refining. By reducing the required temperatures and pressures for reactions, catalysts minimize energy consumption, optimize production rates, and improve the quality of the end products. Moreover, catalysts help control undesired reactions, such as the formation of pollutants, resulting in cleaner and more environmentally friendly processes. Refinery Catalyst can be broadly categorized into four main types based on their applications: hydroprocessing catalysts, fluid catalytic cracking (FCC) catalysts, reforming catalysts, and isomerization catalysts. Hydroprocessing Catalysts: These catalysts play a crucial role in hydrotreating and hydrocracking processes. Hydrotreating removes impurities, such as sulfur and nitrogen, from crude oil, while hydrocracking breaks down heavy hydrocarbon molecules into lighter and more valuable products. Commonly used hydroprocessing catalysts include cobalt-molybdenum or nickel-molybdenum catalysts supported on alumina. Fluid Catalytic Cracking (FCC) Catalysts: FCC catalysts are employed in the fluid catalytic cracking process, which converts heavy oil fractions into lighter, more valuable products like gasoline and olefins. These catalysts, often composed of zeolite and a matrix material, selectively crack larger hydrocarbon molecules into smaller ones. The advancement in FCC catalyst technology has greatly improved conversion efficiency and product yields. Reforming Catalysts: Reforming is a vital process for producing high-octane gasoline and aromatics. Reforming catalysts, such as platinum or platinum-rhenium supported on alumina, promote the rearrangement of hydrocarbon molecules, leading to the desired products. These catalysts help enhance the octane rating of gasoline while minimizing the formation of pollutants. Refinery Catalyst have revolutionized the petroleum industry by enabling refineries to adapt to changing demands, stringent environmental regulations, and the need for increased efficiency. Their impact can be witnessed through the following key aspects: The Refinery Catalyst has emerged as a pivotal force in the petroleum industry, propelling refineries toward increased efficiency, profitability, and sustainability. As catalyst technologies continue to evolve, refineries will benefit from enhanced product quality, energy savings, and the ability to adapt to evolving market demands. With their ability to drive chemical reactions, minimize environmental impact, and enable cleaner energy solutions, refinery catalysts have truly revolutionized the refining landscape, shaping a brighter future for the industry and the world at large. |
|